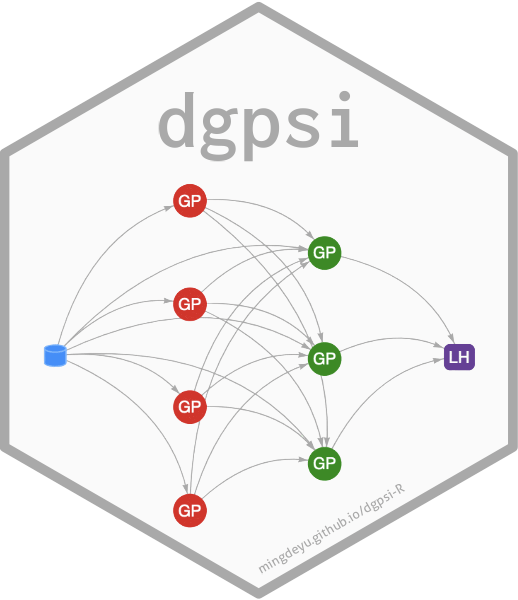
Usage
dgp(
X,
Y,
depth = 2,
node = ncol(X),
name = "sexp",
lengthscale = 1,
bounds = NULL,
prior = "ga",
share = TRUE,
nugget_est = FALSE,
nugget = NULL,
scale_est = TRUE,
scale = 1,
connect = NULL,
likelihood = NULL,
training = TRUE,
verb = TRUE,
check_rep = TRUE,
vecchia = FALSE,
M = 25,
ord = NULL,
N = ifelse(vecchia, 200, 500),
cores = 1,
blocked_gibbs = TRUE,
ess_burn = 10,
burnin = NULL,
B = 10,
id = NULL,
decouple = FALSE,
link = "logit"
)Arguments
- X
a matrix where each row is an input training data point and each column represents an input dimension.
- Y
a matrix containing observed training output data. The matrix has its rows being output data points and columns representing output dimensions. When
likelihood(see below) is notNULL,Ymust be a matrix with a single column.- depth
number of layers (including the likelihood layer) for a DGP structure.
depthmust be at least2. Defaults to2.- node
number of GP nodes in each layer (except for the final layer or the layer feeding the likelihood node) of the DGP. Defaults to
ncol(X).- name
a character or a vector of characters that indicates the kernel functions (either
"sexp"for squared exponential kernel or"matern2.5"for Matérn-2.5 kernel) used in the DGP emulator:if a single character is supplied, the corresponding kernel function will be used for all GP nodes in the DGP hierarchy.
if a vector of characters is supplied, each character of the vector specifies the kernel function that will be applied to all GP nodes in the corresponding layer.
Defaults to
"sexp".- lengthscale
initial lengthscales for GP nodes in the DGP emulator. It can be a single numeric value or a vector:
if it is a single numeric value, the value will be applied as the initial lengthscales for all GP nodes in the DGP hierarchy.
if it is a vector, each element of the vector specifies the initial lengthscales that will be applied to all GP nodes in the corresponding layer. The vector should have a length of
depthiflikelihood = NULLor a length ofdepth - 1iflikelihoodis notNULL.
Defaults to a numeric value of
1.0.- bounds
the lower and upper bounds of lengthscales in GP nodes. It can be a vector or a matrix:
if it is a vector, the lower bound (the first element of the vector) and upper bound (the second element of the vector) will be applied to lengthscales for all GP nodes in the DGP hierarchy.
if it is a matrix, each row of the matrix specifies the lower and upper bounds of lengthscales for all GP nodes in the corresponding layer. The matrix should have its row number equal to
depthiflikelihood = NULLor todepth - 1iflikelihoodis notNULL.
Defaults to
NULLwhere no bounds are specified for the lengthscales.- prior
prior to be used for MAP estimation of lengthscales and nuggets of all GP nodes in the DGP hierarchy:
gamma prior (
"ga"),inverse gamma prior (
"inv_ga"), orjointly robust prior (
"ref").
Defaults to
"ga".a bool indicating if all input dimensions of a GP node share a common lengthscale. Defaults to
TRUE.- nugget_est
a bool or a bool vector indicating whether the nuggets of GP nodes in the final layer (or the layer feeding the likelihood node) should be estimated. If a bool is provided, it is applied to all GP nodes in that layer. If a bool vector is provided, its length must match the number of GP nodes:
ncol(Y)iflikelihood = NULL2iflikelihoodis"Hetero"or"NegBin"1iflikelihoodis"Poisson"or"Categorical"with two classesthe number of classes if
likelihoodis"Categorical"with more than two classes.
Each element of the vector is applied to the corresponding GP node in the final layer (or the layer feeding the likelihood node). The value of a bool has following effects:
FALSE: the nugget of the corresponding GP is fixed to the corresponding value defined innugget(see below).TRUE: the nugget of the corresponding GP will be estimated with the initial value given by the correspondence innugget(see below).
Defaults to
FALSE.- nugget
the initial nugget value(s) of GP nodes (if any) in each layer:
if it is a single numeric value, the value will be applied as the initial nugget for all GP nodes in the DGP hierarchy.
if it is a vector, each element of the vector specifies the initial nugget that will be applied to all GP nodes in the corresponding layer. The vector should have a length of
depthiflikelihood = NULLor a length ofdepth - 1iflikelihoodis notNULL.
Set
nuggetto a small value and the bools innugget_esttoFALSEfor deterministic emulation, where the emulator interpolates the training data points. Setnuggetto a larger value and the bools innugget_esttoTRUEfor stochastic emulation where the computer model outputs are assumed to follow a homogeneous Gaussian distribution. Defaults to1e-6iflikelihoodisNULL. Iflikelihoodis notNULL, the nuggets of GPs that feed into the likelihood layer default to1e-4, while those of all other GPs default to1e-6.- scale_est
a bool or a bool vector indicating whether the variances of GP nodes in the final layer (or the layer feeding the likelihood node) should be estimated. If a bool is provided, it is applied to all GP nodes in that layer. If a bool vector is provided, its length must match the number of GP nodes:
ncol(Y)iflikelihood = NULL2iflikelihoodis"Hetero"or"NegBin"1iflikelihoodis"Poisson"or"Categorical"with two classesthe number of classes if
likelihoodis"Categorical"with more than two classes.
The value of a bool has following effects:
FALSE: the variance of the corresponding GP is fixed to the corresponding value defined inscale(see below).TRUE: the variance of the corresponding GP will be estimated with the initial value given by the correspondence inscale(see below).
Defaults to
TRUE.- scale
the initial variance value(s) of GP nodes in the final layer (or the layer feeding the likelihood node). If it is a single numeric value, it will be applied to all GP nodes in the final layer (or the layer feeding the likelihood node). If it is a vector, its length must match the number of GP nodes:
ncol(Y)iflikelihood = NULL2iflikelihoodis"Hetero"or"NegBin"1iflikelihoodis"Poisson"or"Categorical"with two classesthe number of classes if
likelihoodis"Categorical"with more than two classes.
Each numeric in the vector will be applied to the corresponding GP node.
Defaults to
1.- connect
a bool indicating whether to apply global input connections in the DGP structure. Setting this to
FALSEmay yield a better emulator in some cases. When set toNULL, the value defaults toFALSEiflikelihood = "Categorical"and toTRUEotherwise. Defaults toNULL.- likelihood
the likelihood type of a DGP emulator:
NULL: no likelihood layer is included in the emulator."Hetero": a heteroskedastic Gaussian likelihood layer is added for stochastic emulation where the computer model outputs are assumed to follow a heteroskedastic Gaussian distribution (i.e., the computer model outputs have input-dependent noise)."Poisson": a Poisson likelihood layer is added for emulation where the computer model outputs are counts and a Poisson distribution is used to model them."NegBin": a negative Binomial likelihood layer is added for emulation where the computer model outputs are counts and a negative Binomial distribution is used to capture dispersion variability in input space."Categorical": a categorical likelihood layer is added for emulation (classification), where the computer model output is categorical.
Defaults to
NULL.- training
a bool indicating if the initialized DGP emulator will be trained. When set to
FALSE,dgp()returns an untrained DGP emulator, to which one can applysummary()to inspect its specifications or applypredict()to check its emulation performance before training. Defaults toTRUE.- verb
a bool indicating if the trace information on DGP emulator construction and training will be printed during the function execution. Defaults to
TRUE.- check_rep
a bool indicating whether to check for repetitions in the dataset, i.e., if one input position has multiple outputs. Defaults to
TRUE.- vecchia
a bool indicating whether to use Vecchia approximation for large-scale DGP emulator construction and prediction. Defaults to
FALSE.- M
the size of the conditioning set for the Vecchia approximation in the DGP emulator training. Defaults to
25.- ord
an R function that returns the ordering of the input to each GP node contained in the DGP emulator for the Vecchia approximation. The function must satisfy the following basic rules:
the first argument represents the input to a GP node scaled by its lengthscales.
the output of the function is a vector of indices that gives the ordering of the input to the GP node.
If
ord = NULL, the default random ordering is used. Defaults toNULL.- N
number of iterations for the training. Defaults to
500ifvecchia = FALSEand200ifvecchia = TRUE. This argument is only used whentraining = TRUE.- cores
the number of processes to be used to optimize GP components (in the same layer) at each M-step of the training. If set to
NULL, the number of processes is set to(max physical cores available - 1)ifvecchia = FALSEandmax physical cores available %/% 2ifvecchia = TRUE. Only use multiple processes when there is a large number of GP components in different layers and optimization of GP components is computationally expensive. Defaults to1.- blocked_gibbs
a bool indicating if the latent variables are imputed layer-wise using ESS-within-Blocked-Gibbs. ESS-within-Blocked-Gibbs would be faster and more efficient than ESS-within-Gibbs that imputes latent variables node-wise because it reduces the number of components to be sampled during Gibbs steps, especially when there is a large number of GP nodes in layers due to higher input dimensions. Default to
TRUE.- ess_burn
number of burnin steps for the ESS-within-Gibbs at each I-step of the training. Defaults to
10. This argument is only used whentraining = TRUE.- burnin
the number of training iterations to be discarded for point estimates of model parameters. Must be smaller than the training iterations
N. If this is not specified, only the last 25% of iterations are used. Defaults toNULL. This argument is only used whentraining = TRUE.- B
the number of imputations used to produce predictions. Increase the value to refine the representation of imputation uncertainty. Defaults to
10.- id
an ID to be assigned to the DGP emulator. If an ID is not provided (i.e.,
id = NULL), a UUID (Universally Unique Identifier) will be automatically generated and assigned to the emulator. Default toNULL.- decouple
A boolean indicating whether the model parameters for the heteroskedastic Gaussian likelihood, negative Binomial likelihood, and categorical likelihood (when the number of categories is greater than 2) should be modeled using separate deep Gaussian process hierarchies when
depthis greater than 2. Defaults toFALSE.- link
the link function used for binary classification when
likelihood = "Categorical". Supported options are"logit"and"probit". Defaults to"logit".
Value
An S3 class named dgp that contains five slots:
id: A number or character string assigned through theidargument.data: a list that contains two elements:XandYwhich are the training input and output data respectively.specs: a list that containsL (i.e., the number of layers in the DGP hierarchy) sub-lists named
layer1, layer2,..., layerL. Each sub-list contains D (i.e., the number of GP/likelihood nodes in the corresponding layer) sub-lists namednode1, node2,..., nodeD. If a sub-list corresponds to a likelihood node, it contains one element calledtypethat gives the name (Hetero,Poisson,NegBin, orCategorical) of the likelihood node. If a sub-list corresponds to a GP node, it contains four elements:kernel: the type of the kernel function used for the GP node.lengthscales: a vector of lengthscales in the kernel function.scale: the variance value in the kernel function.nugget: the nugget value in the kernel function.
seed: the random seed generated to produce imputations. This information is stored for reproducibility when the DGP emulator (that was saved bywrite()with the light optionlight = TRUE) is loaded back to R byread().B: the number of imputations used to generate the emulator.vecchia: whether the Vecchia approximation is used for the GP emulator training.M: the size of the conditioning set for the Vecchia approximation in the DGP emulator training.Mis generated only whenvecchia = TRUE.
constructor_obj: a 'python' object that stores the information of the constructed DGP emulator.container_obj: a 'python' object that stores the information for the linked emulation.emulator_obj: a 'python' object that stores the information for the predictions from the DGP emulator.
The returned dgp object can be used by
predict()for DGP predictions.continue()for additional DGP training iterations.validate()for LOO and OOS validations.plot()for validation plots.lgp()for linked (D)GP emulator constructions.window()for model parameter trimming.summary()to summarize the trained DGP emulator.write()to save the DGP emulator to a.pklfile.set_imp()to change the number of imputations.design()for sequential design.update()to update the DGP emulator with new inputs and outputs.
Details
See further examples and tutorials at https://mingdeyu.github.io/dgpsi-R/.
Note
Any R vector detected in X and Y will be treated as a column vector and automatically converted into a single-column
R matrix. Thus, if X is a single data point with multiple dimensions, it must be given as a matrix.
Examples
if (FALSE) { # \dontrun{
# load the package and the Python env
library(dgpsi)
# construct a step function
f <- function(x) {
if (x < 0.5) return(-1)
if (x >= 0.5) return(1)
}
# generate training data
X <- seq(0, 1, length = 10)
Y <- sapply(X, f)
# set a random seed
set_seed(999)
# training a DGP emulator
m <- dgp(X, Y)
# continue for further training iterations
m <- continue(m)
# summarizing
summary(m)
# trace plot
trace_plot(m)
# trim the traces of model parameters
m <- window(m, 800)
# LOO cross validation
m <- validate(m)
plot(m)
# prediction
test_x <- seq(0, 1, length = 200)
m <- predict(m, x = test_x)
# OOS validation
validate_x <- sample(test_x, 10)
validate_y <- sapply(validate_x, f)
plot(m, validate_x, validate_y)
# write and read the constructed emulator
write(m, 'step_dgp')
m <- read('step_dgp')
} # }